One, Introduction
The Eaton electromagnetic servo valve, as an indispensable part of the automation system, directly affects the stability and accuracy of the system. This article will discuss the principle, classification, selection criteria, and application fields of the electromagnetic servo valve to help users better understand and select the appropriate electromagnetic servo valve.
Two, Principle of electromagnetic servo valve
The electromagnetic servo valve is a valve driven by an electromagnetic coil, whose working principle is to use the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnetic coil to overcome the spring force, drive the valve core to move, and thus change the direction of the fluid. The electromagnetic servo valve is widely used in automation control systems, and through precise control of the fluid flow, pressure, and direction, it can achieve accurate control of the actuator.
Three, Classification of electromagnetic servo valves
Categorization by working principle: Including direct-acting and pilot electromagnetic servo valves. The direct-acting electromagnetic servo valve does not require a pilot electromagnetic coil, has a simple structure, and has a fast response speed, but has relatively lower control accuracy; the pilot electromagnetic servo valve drives the main valve core through the pilot electromagnetic coil, has higher control accuracy and response speed.
Categorization by control method: Including voltage control and current control electromagnetic servo valves. The voltage control electromagnetic servo valve controls the movement of the valve core by changing the input voltage; the current control electromagnetic servo valve controls the movement of the valve core by changing the input current.
Categorization by installation method: Including right-angle and direct-flow electromagnetic servo valves. The right-angle electromagnetic servo valve is suitable for applications that require changing the fluid direction; the direct-flow electromagnetic servo valve is suitable for applications that require changing the fluid direction.
Four, Selection criteria for electromagnetic servo valves
Flow demand: Choose a suitable electromagnetic servo valve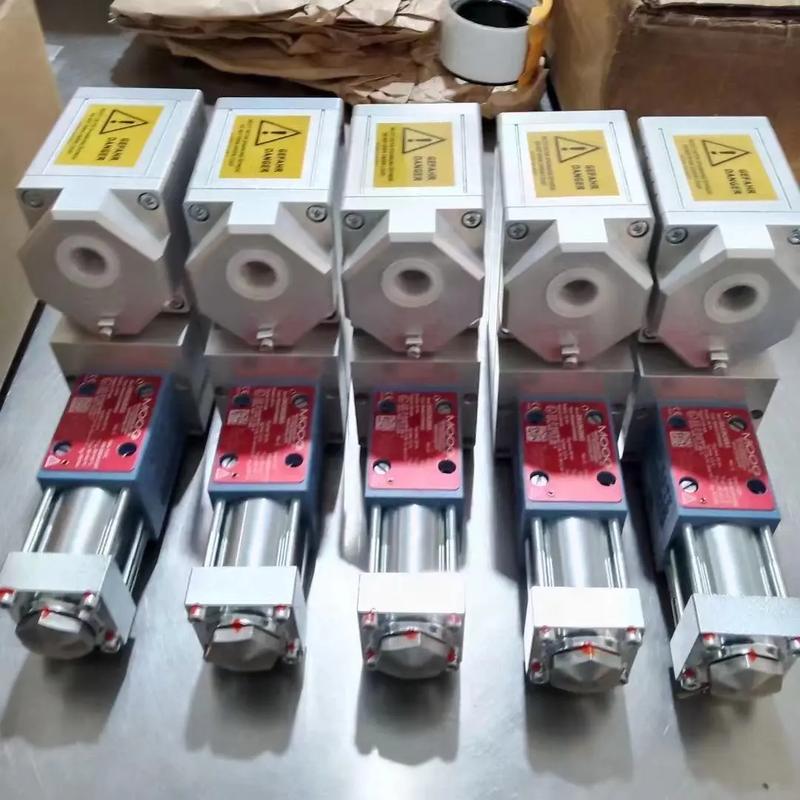 according to the system's demand for fluid flow.
according to the system's demand for fluid flow.
Pressure demand: Choose a suitable electromagnetic servo valve according to the system's demand for fluid pressure.
Control accuracy: Choose a suitable electromagnetic servo valve according to the system's requirements for control accuracy.
Working environment: Choose a suitable electromagnetic servo valve according to the working environment of the electromagnetic servo valve.
suitable electromagnetic servo valve according to the working environment of the electromagnetic servo valve.
Rated voltage: Choose a suitable electromagnetic servo valve according to the rated voltage provided by the system.
Five, Application fields of electromagnetic servo valves
Automotive industry: In the process of car manufacturing, the electromagnetic servo valve is used to control injectors, exhaust valves, and other actuators to ensure the stable operation of the engine.
Robotics technology: In industrial robots, the electromagnetic servo valve is used to control pneumatic or hydraulic actuators to achieve precise motion control.
Electronic equipment: In electronic equipment, the electromagnetic servo valve is used to control pneumatic or hydraulic actuators to achieve precise motion control.
Medical equipment: In medical equipment, the electromagnetic servo valve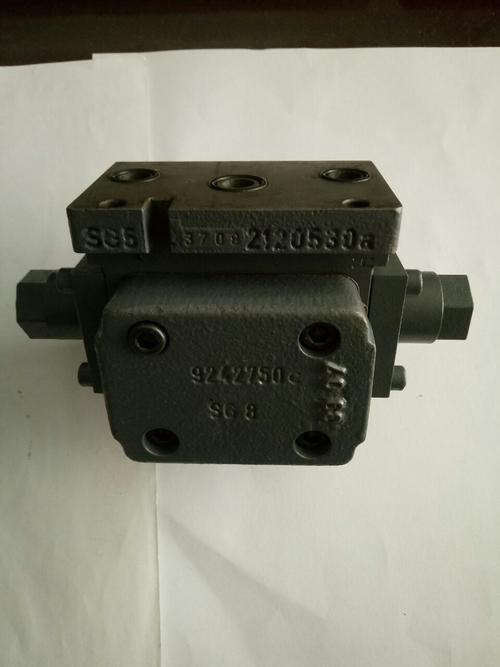 is used to control pneumatic or hydraulic actuators to achieve precise motion control.
is used to control pneumatic or hydraulic actuators to achieve precise motion control.
Six, Conclusion
The electromagnetic servo valve, as an indispensable part of the automation system, directly affects the stability and accuracy of the system. Proper selection and use of the electromagnetic servo valve are of great significance for improving the performance of the automation system. It is hoped that this article can provide users with certain reference value.